eDNA Metabarcoding
Discover the future of biodiversity monitoring with environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding. This innovative technology enables rapid, non-invasive detection of species from water, soil, or air samples. At Cmbio, we provide advanced eDNA solutions using long read sequencing techniques that empower environmental consultants, researchers, and regulators to achieve accurate, efficient, and scalable biodiversity assessments for conservation, compliance, and ecological research.
eDNA metabarcoding offers a robust alternative to traditional environmental surveys by allowing direct DNA-based detection of organisms within complex ecosystems. By analysing biological material collected from diverse habitat types, our solutions help uncover detailed information about species richness, relative abundance, taxonomic groups and community structure, even under changing conditions and human activities.
Superior detection capabilities
eDNA metabarcoding detects rare, elusive, or cryptic species that traditional methods often miss - identifying 2–10 times more species from a single environmental sample. This comprehensive approach enables early detection of invasive species and environmental threats.
Using eDNA data collected from marine systems, freshwater, or terrestrial environments, subsequent analysis provides insight into spatial patterns, species present, and their current conservation status. This is especially valuable for assessing natural range shifts due to climate change or the impact of surrounding area disturbances.
Faster, affordable, and scalable
Experience proven cost savings of 30–60% compared to conventional surveys, with over 80% reduction in labor hours. eDNA scales efficiently for projects of any size - making large-scale biodiversity monitoring more accessible than ever.
Environmental DNA metabarcoding allows researchers to analyse food webs, monitor ecosystem health, and compare biodiversity levels across regions or time periods—all from a single sample. Our workflows include precise sample collection, DNA extraction, and next generation sequencing for unmatched scalability and speed in environmental monitoring and data analysis.
Strict environmental standards
Our eDNA solutions support biodiversity monitoring requirements under EU directives (including Annex II and IV species), ensuring regulatory compliance. The non-invasive sampling process eliminates the need for physical capture or disturbance, protecting both species and habitats.
Through alignment with the guidance of Habitats Directive and Birds Directive, our services assist with evaluating favourable conservation status, maintaining protected areas, and monitoring species listed under legal conservation frameworks. This contributes to long-term planning and resilience in biodiversity conservation across the European Union.
What is eDNA metabarcoding?
eDNA metabarcoding is a cutting-edge molecular technique that enables the identification of multiple species from environmental samples - such as water, soil, or air - by analyzing DNA fragments shed by organisms into their surroundings. Using advanced long read sequencing technologies, this approach allows for non-invasive, large-scale biodiversity monitoring, surpassing the limitations of traditional survey methods.
In contrast to conventional techniques like Sanger sequencing, which typically focus on individual organisms or whole cells, eDNA metabarcoding offers a rapid, cost-effective tool for detecting many different species simultaneously, even at low relative abundance. Combined with comprehensive reference databases, this makes it ideal for assessing species richness in complex ecosystems.
Who can benefit?
Traditional biodiversity surveys often require repeated field visits, labor-intensive trapping, netting, and expert specimen identification, making them time-consuming and costly. eDNA streamlines or eliminates these steps by enabling direct species detection from simple water, soil, or air samples - offering faster, more cost-effective, and comprehensive biodiversity insights.
By simplifying and accelerating the monitoring process, eDNA greatly benefits those involved in:
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Pre- and post-project biodiversity evaluation for construction, agriculture, aquaculture, mining, and forestry sectors.
- Biodiversity Assessment: Baseline surveys and long-term monitoring of ecosystems. Environmental data from eDNA surveys supports consistent biodiversity tracking across time and space.
- Conservation Biology: Detection of threatened species, invasive species, and indicators of ecosystem health. This can include rare species that are hard to detect with traditional methods.
- Regulatory Compliance: Monitoring for Annex II and Annex IV species under EU Habitats Directive and Birds Directive, contributing to assessments of favourable conservation status and habitat integrity.
- Ecological Research: Community composition studies, food web dynamics, species distribution modelling, and evaluation of future changes in biodiversity.
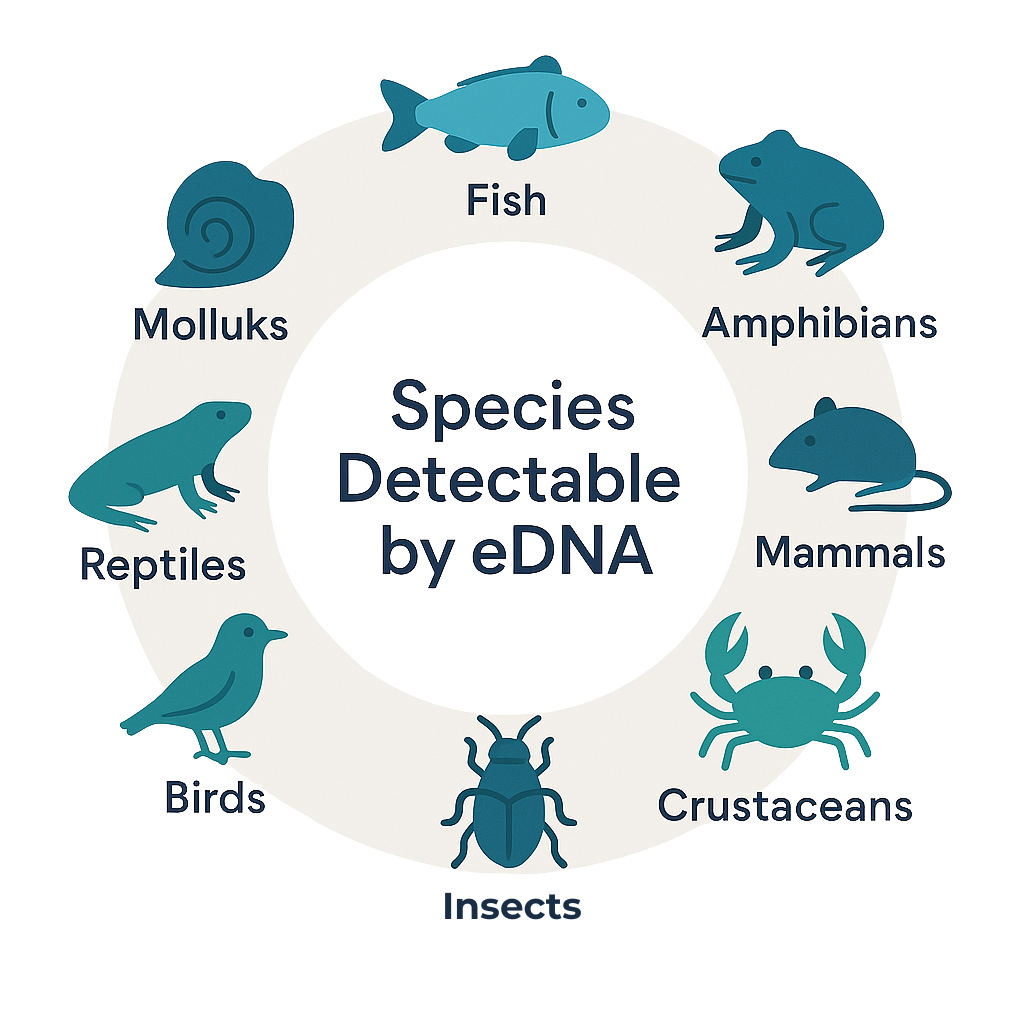
How does it work?
Our process begins with the careful sample collection of water, soil, or air from the target site. These environmental samples contain traces of DNA shed by organisms through skin, scales, feathers, waste, or decaying tissue. After DNA extraction, we use high-throughput next generation sequencing to amplify specific DNA regions.
This enables the detection of which species inhabit a sample—including those that are rare, cryptic, or migratory—without needing to see or capture them. Our laboratory workflows are designed to minimise contamination, and we apply advanced data analysis techniques to interpret the DNA results within ecological and regulatory contexts.
These insights power research projects, conservation planning, and biodiversity monitoring programmes worldwide, supported by emerging technologies that continue to evolve the capabilities of environmental DNA science.
.png?width=2000&height=625&name=eDNA%20process%20(1).png)